Type 2 Diabetes After Pregnancy
For many new mothers, the joy of childbirth is often accompanied by health concerns. One such concern is the development of type 2 diabetes
after pregnancy. Are you experiencing elevated blood sugar levels even after delivering your baby? Don’t worry! Diabetes after pregnancy can be effectively managed with the proper guidance.
Dr. Ayush Chandra, a highly regarded diabetologist in Ghaziabad, advises that understanding this condition and recognizing its symptoms is crucial for overall well-being. Women who have gestational diabetes should monitor their blood sugar after pregnancy. Early diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan can significantly reduce the impact of this condition.
Dr. Ayush Chandra has 14+ years of experience in managing diabetes, particularly post-pregnancy cases. He has helped countless women regain control of their health by providing personalized diabetes treatment in Ghaziabad. His expertise ensures patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their needs and effective management strategies.

Now, let’s explore the reasons behind high levels of sugar after pregnancy.
Causes and Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes After Pregnancy
-
- Gestational Diabetes: Women who had gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes later.
-
- Family History: A family history of diabetes can increase susceptibility to developing this condition.
-
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, contributes to insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to manage blood sugar levels.
-
- Age: Women over the age of 25 are more prone to develop Type 2 Diabetes after pregnancy.
-
- Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance.
-
- Diet: Poor dietary choices, such as high sugar and low fibre intake, can increase blood sugar levels.
-
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy can cause hormonal shifts affecting blood sugar regulation.
Are you experiencing unusual symptoms post-pregnancy? It’s essential to identify signs that may indicate Type 2 Diabetes.
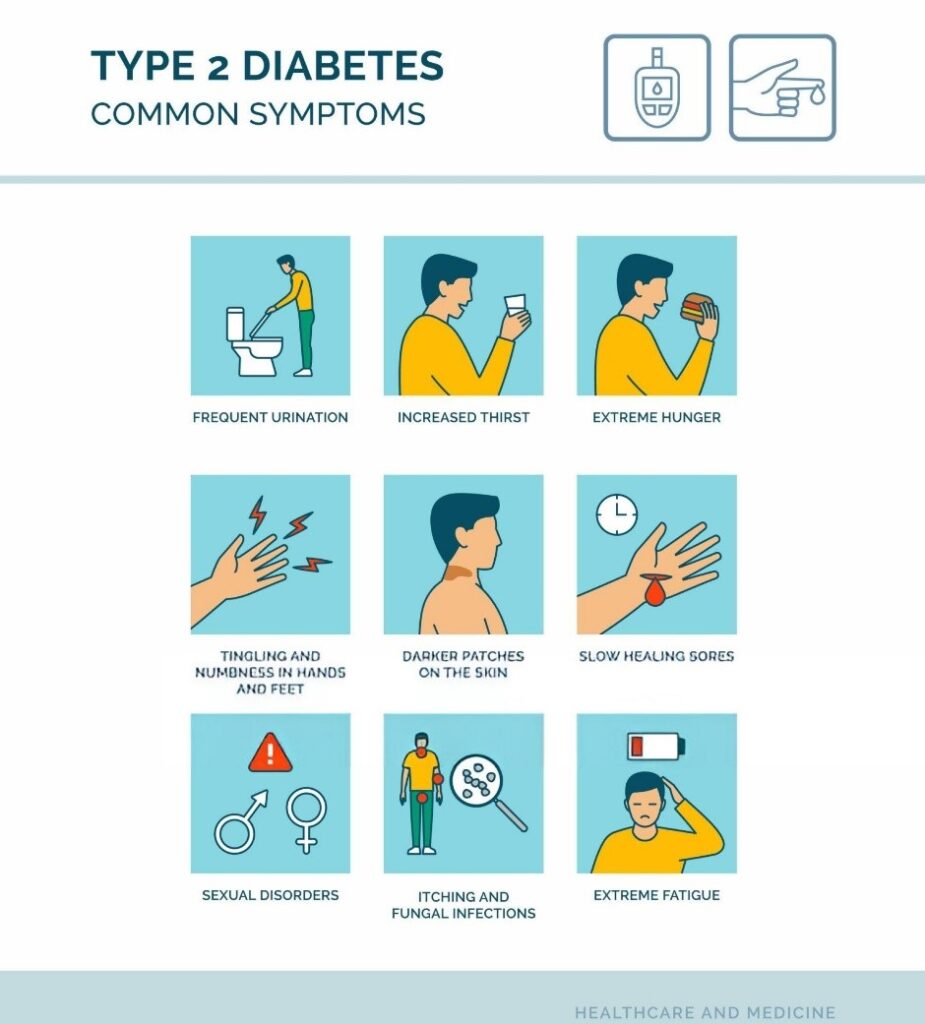
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
-
- Increased Thirst: A persistent feeling of thirst can indicate high blood sugar levels.
-
- Frequent Urination: Needing to urinate more often than usual is another common symptom.
-
- Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired or lethargic can indicate issues with blood sugar regulation.
-
- Blurred Vision: Changes in vision, especially blurred eyesight, may occur due to high blood sugar.
-
- Slow Healing Wounds: If cuts or bruises take longer to heal, it could signal a problem with blood sugar levels.
-
- Weight Changes: Unexplained weight loss or gain can also be a sign of diabetes.
These symptoms can be subtle and may develop gradually. So, it is essential to monitor any changes in your health after delivery.
Are you noticing any of these symptoms? Consult an expert today and get your blood sugar levels checked. Schedule your appointment now!
Do you know how Type 2 Diabetes can affect your overall health? Understanding the implications can help you stay healthy.
How Type 2 Diabetes After Pregnancy Affects Your Health
Type 2 Diabetes can have long-term effects on your health if left unmanaged. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, leading to cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, kidney problems, and vision issues. Women with diabetes after pregnancy may also face difficulties with weight management, which can worsen insulin resistance and increase the risk of complications.
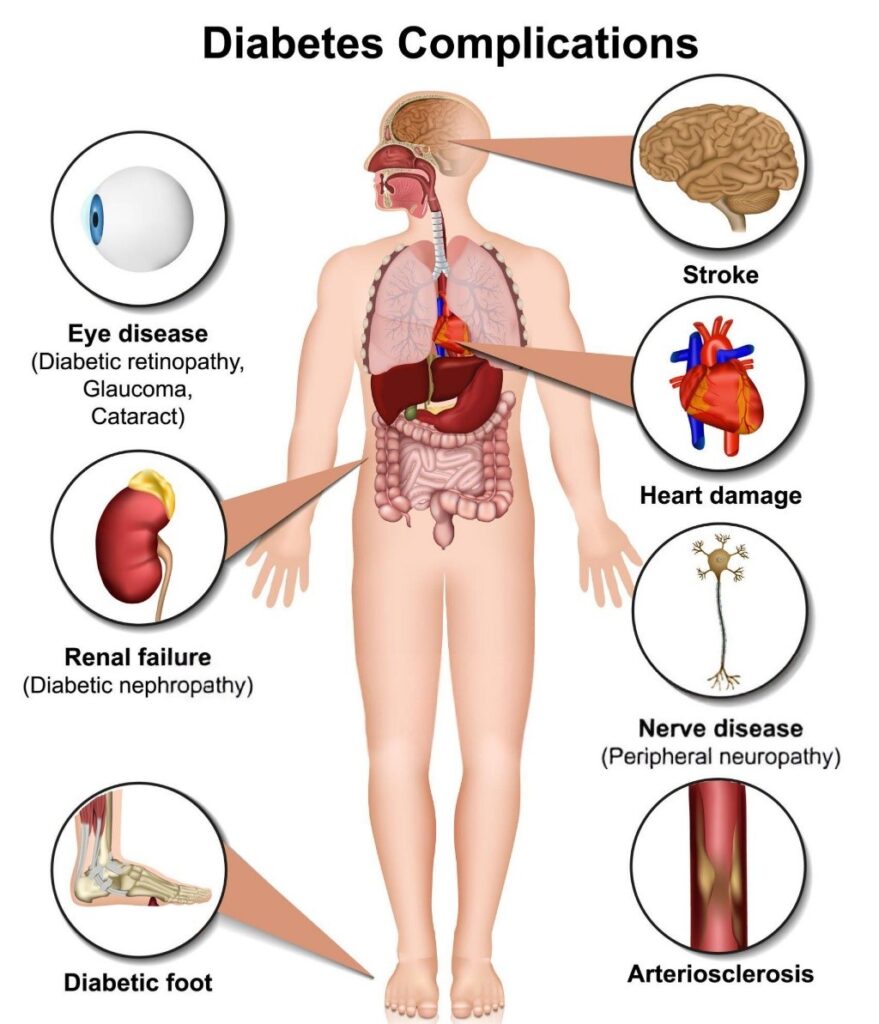
Moreover, the hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy and after childbirth can make it more challenging to manage diabetes. Without proper care, diabetes can significantly affect your quality of life, including your energy levels, mental health, and overall well-being. However, with the right approach to diabetes management, including lifestyle modifications and medical care, you can effectively control your blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
How can you effectively manage Type 2 Diabetes after pregnancy? Implementing the right strategies is crucial for your health.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes After Pregnancy

-
- Monitor Blood Sugar:
Check blood sugar levels regularly to monitor fluctuations and prevent complications. Monitoring is crucial after pregnancy to avoid further issues.
Eat a balanced diet with whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks to prevent blood sugar spikes.
-
- Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity like walking or light cardio to improve insulin sensitivity and help manage blood sugar.
-
- Medication and Insulin:
Some women may need medication or insulin; follow medical guidance on dosage and frequency.
Use relaxation techniques like meditation or Yoga to control stress, which can affect blood sugar levels.
-
- Regular Check-ups:
Consistent follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure your diabetes management plan stays effective.
Adopting these habits can significantly help manage and even prevent type 2 diabetes after pregnancy and ensure long-term health.
Are you unsure when to consult a doctor about your health? Let’s explore.
When to Consult a Doctor

Recognizing when to seek medical advice about type 2 diabetes after pregnancy is critical. Here are vital situations where consulting a doctor is essential:
-
- Persistent High Blood Sugar:
If your blood sugar level after delivery stays elevated, seek immediate medical attention to prevent complications.
-
- Unexplained Fatigue:
Feeling unusually tired or weak despite sufficient rest could signal type 2 diabetes. Consult a doctor to confirm or rule out the condition.
-
- Frequent Urination and Thirst:
These common diabetes symptoms warrant a specialist’s evaluation if they occur often.
-
- Sudden Vision Changes:
Blurred vision or other changes in eyesight may indicate fluctuating blood sugar and need prompt medical attention.
-
- Unintended Weight Loss:
Unexpected weight loss, especially with other symptoms like hunger or frequent urination, should be assessed by a doctor.
Conclusion
Type 2 Diabetes after pregnancy is a manageable condition with the proper care and support. By working with a diabetes expert, women can take control of their health and reduce the long-term risks associated with this condition. Dr. Ayush Chandra, a renowned diabetologist in Ghaziabad, offers personalized treatment plans to help individuals control their diabetes effectively.
Consult a seasoned expert to manage your health after pregnancy and get the right advice to keep your blood sugar in check. Book your appointment today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you get Type 2 diabetes after pregnancy?
Yes, women who experience gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes after pregnancy.
Why does pregnancy cause Type 2 diabetes?
Pregnancy causes hormonal changes that can increase insulin resistance, making it harder for your body to regulate blood sugar levels.
How to test for diabetes after pregnancy?
A doctor may recommend an oral glucose tolerance or fasting blood sugar test to check for diabetes after pregnancy.
How common is diabetes after pregnancy?
Women with gestational diabetes have a 50% higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes within 5-10 years after delivery.
Is it possible to reverse Type 2 diabetes after pregnancy?
While Type 2 diabetes can be managed and blood sugar level after pregnancy can be normalized through lifestyle changes, it may not be entirely reversible for everyone.
Reference links:
https://www.spectrumhealthlakeland.org/lakeland-diabetes/diabetes-health-library/Content/3/61015
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/gestational-diabetes
Disclaimer: This page is for informational purposes and not for promotional u


