Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) in Ghaziabad
Living with diabetes can be challenging, especially when it comes to maintaining stable glucose levels. Uncontrolled blood sugar can lead to serious health issues, making regular glucose tracking essential. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems are a revolutionary tool that provides a comprehensive way to track blood sugar levels in real-time, enabling better control and reducing the risk of complications.
Dr. Ayush Chandra, a highly regarded diabetologist in Ghaziabad, states, “CGM empowers patients with actionable insights into their glucose patterns, significantly improving diabetes management.”
Dr. Chandra is well-known for offering advanced diabetes care utilizing cutting-edge technology like Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) in Ghaziabad.
With over 14 years of expertise, he assists patients in maintaining stable blood sugar levels through personalized approaches to minimize diabetes-related complications and enhance overall health.
To learn more about CGM devices and their role in effective diabetes management, please scroll down.
What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)?
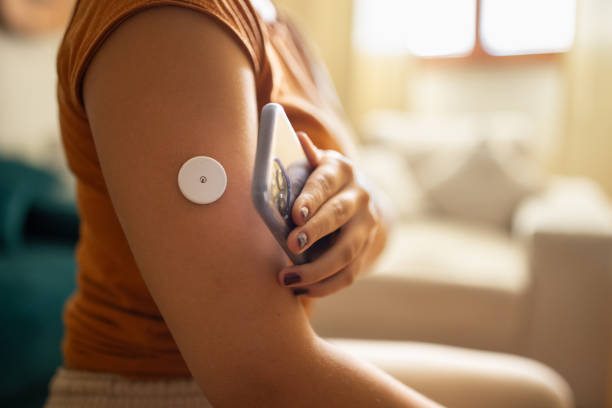
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is an advanced tool for tracking blood sugar levels 24/7. Unlike traditional finger-prick tests, the CGM system uses a sensor placed under the skin that records glucose levels every few minutes. This less invasive method is especially helpful for individuals requiring intensive glucose management.
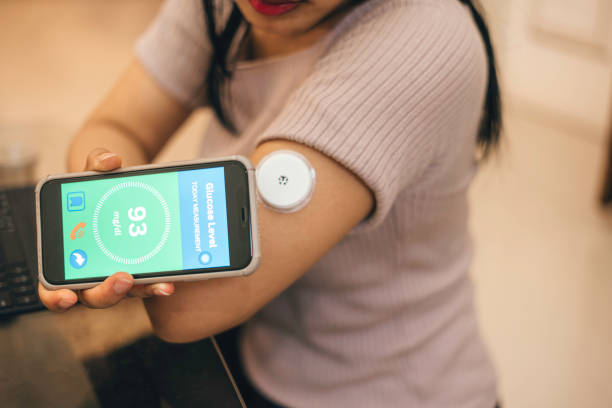
CGM data can be synced to smartphones, providing easy access to readings, trends, and alerts. Healthcare providers can use this information to customize treatment plans, identify triggers for fluctuations, and suggest lifestyle changes. Patients can modify their diets, activities, or medications based on these insights, leading to more precise diabetes management.
Let’s discover the significance of CGM in diabetes care.
Why is Continuous Glucose Monitoring Important?
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is crucial for individuals with frequent blood sugar fluctuations. It allows patients to track their glucose levels continuously, offering more precision than traditional blood tests. This is particularly beneficial for those with diabetes who use insulin or find standard monitoring methods challenging.
CGM devices alert users to low or high blood sugar levels, helping prevent emergencies and enabling timely adjustments for better safety and health. Studies show that using CGM often leads to improved glycemic control, reducing the risk of complications like heart disease, kidney issues, and nerve damage.
Discover how CGM can transform diabetes management. Consult an expert diabetologist to start monitoring your glucose levels effectively. Book an appointment now!
Wondering about the different CGM options available? Let’s dive in.
Types of CGM Devices
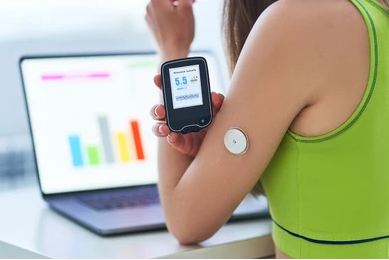
Real-Time CGM (rtCGM): Real-time CGM devices continuously monitor glucose levels and provide immediate, real-time data to the user. Alerts for high or low levels make it ideal for those needing instant monitoring.
Intermittent Scanning CGM (isCGM): Intermittent scanning CGMs, often referred to as “flash” CGMs, allow users to scan a sensor to get glucose data rather than providing constant updates. It’s an excellent option for users who don’t need real-time alerts.
Professional CGM: These are typically used by healthcare providers for short-term monitoring, often for a few days to a week. It provides data to support in-depth consultations without requiring continuous use.
Integrated CGM (iCGM): Integrated CGMs are approved to work with other devices like insulin pumps, creating a seamless connection between monitoring and insulin delivery. This type is ideal for individuals needing automated insulin adjustments.
Now, let’s understand how these devices actually function.
How Does CGM Work?
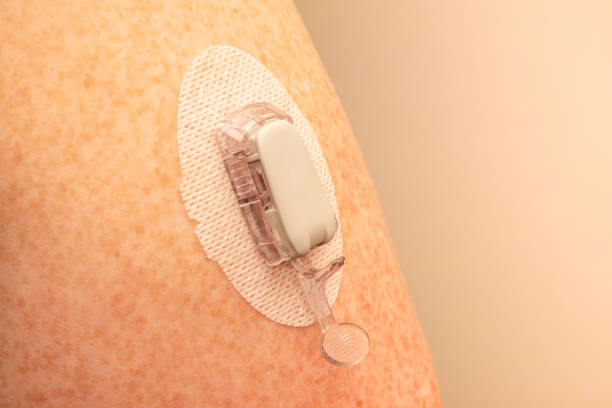
Sensor Insertion: A small sensor is inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen or upper arm, to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The insertion is quick and designed to minimize discomfort.
Continuous Glucose Data Collection: The sensor monitors glucose levels and records data at regular intervals, often every few minutes.
Data Transmission: The sensor transmits glucose readings wirelessly to a compatible device, like a smartphone or a dedicated monitor. This allows users to see real-time data on their current glucose levels.
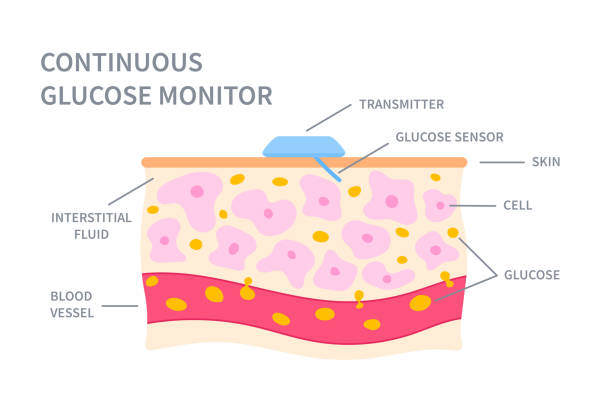
Alerts and Notifications: Many CGM systems offer customizable alerts to notify users of high or low glucose levels, making it easier to take preventive actions.
Data Analysis and Trends: Users can view trends, patterns, and historical data. It helps them make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
Integration with Other Devices: Some CGM systems integrate with insulin pumps, allowing for automatic insulin adjustments based on glucose readings, particularly beneficial for people with Type 1 diabetes.
Reach out to a specialist to explore the right CGM device that suits your lifestyle and needs. Schedule a consultation today!
Looking for the pros and cons of CGM? Here’s what to know.
CGM Benefits and Limitations
Benefits:
Real-Time Monitoring: Provides continuous glucose data, helping to avoid sudden highs or lows.
Improved Diabetes Management: Helps users make timely adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication.
Trend Tracking: Shows glucose trends over time, making it easier to understand patterns.
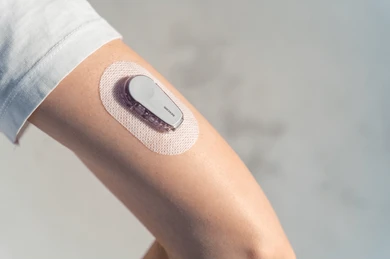
Alerts: Offers alerts for high or low blood sugar, improving early intervention.
Reduced Fingersticks: Reduces the need for frequent blood glucose testing via fingersticks.
Benefits:
Accuracy Issues: Can occasionally provide inaccurate readings, especially if not calibrated properly.
Sensor Replacement: Sensors need to be replaced regularly, which can be inconvenient or costly.
Skin Irritation: Some users may experience irritation or discomfort at the sensor insertion site.
Expense: CGM systems can be expensive, and insurance coverage may be limited.
Battery Dependency: Requires battery-powered devices, which may need recharging or replacement.
Unsure about sensor placement and device training? Let’s clarify the process.
Sensor Insertion and Device Training
- Sensor Insertion
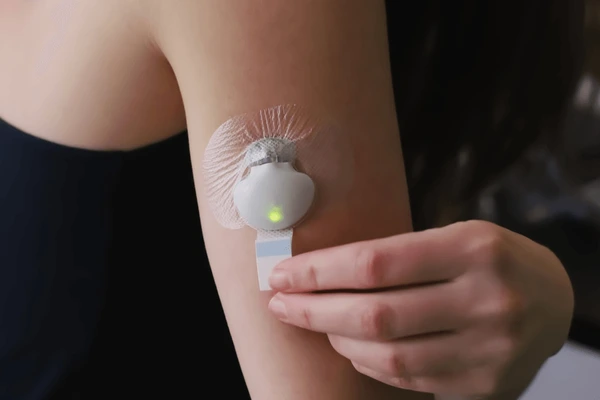
Location Selection: The sensor is typically inserted on the abdomen, upper arm, or other recommended sites.
Procedure: A small needle is used to insert the sensor just under the skin. The needle is removed, leaving the sensor in place.
Application of Adhesive Patch: A sticky adhesive patch secures the sensor to the skin, ensuring it stays in place throughout use.
Discomfort: The insertion process is generally quick and should not cause significant pain.
- Device Training
User Instructions: Dr. Ayush Chandra conducts training sessions to explain the use of the CGM device, including how to insert the sensor, read the data, and interpret glucose trends.
Troubleshooting Tips: Users learn how to troubleshoot common issues, such as poor signal quality or calibration problems.
Connecting to Devices: Users are trained to sync and use the integration features if the CGM device connects to other devices (like a smartphone or insulin pump).
Regular Updates: Some CGM devices may require software updates. Users are guided through updating their systems to ensure they have the latest features and improvements.
Support Contact Information: Users are provided with contact information for support in case they have questions or issues with their CGM device.
Why Choose Dr. Ayush Chandra for CGM?
Expertise in Diabetes Management: Dr. Ayush Chandra has extensive experience managing diabetes and its complications, including through advanced technologies like Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) in Ghaziabad.
Personalized Care: He tailors CGM use to each patient's individual needs, ensuring optimal results and effective diabetes management.
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment: As a seasoned diabetologist, Dr. Chandra provides comprehensive care, including diabetes treatment, obesity management, and diabetic diet nutrition in Ghaziabad, all integrated with CGM technology for better control.
Advanced Technology: Dr. Chandra stays up-to-date with the latest in CGM technology, offering patients access to cutting-edge devices and insights for improved glucose management.

Holistic Approach: He focuses on preventing and managing complications, ensuring patients benefit from CGM and a well-rounded treatment plan.
Choosing the right specialist can make all the difference in diabetes care, from accurate diagnosis to personalized monitoring plans. Book a consultation with a professional today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Not everyone with Type 2 diabetes requires CGM. However, it can help individuals who struggle with managing glucose levels or have frequent fluctuations. It is particularly useful for those on insulin or other medications that affect glucose levels.
Most CGM sensors can be worn for 7 to 14 days, depending on the brand and model. After that, they need replacement to ensure accurate readings.
The insertion process is generally not painful. A small needle is used to insert the sensor just under the skin. Some mild discomfort may occur, but it typically subsides quickly.
CGMs are suitable for children with diabetes, especially those with Type 1 diabetes. A healthcare professional can help determine the appropriate age and provide guidance on their use.

