Heart diseases remain the leading cause of death in the world, accounting for almost 18 million deaths annually, states the World Health Organization. Among the major causes that add to this burden is high cholesterol. Globally, about 39% of adults have elevated cholesterol, and in India, too, the situation is grim-studies show more than 25% of urban adults and 13% of rural adults suffer from hypercholesterolemia, a disease that usually progresses without symptoms.
Dr. Ayush Chandra, an accomplished Diabetologist in Ghaziabad, explains:
“Heart health forms the cornerstone of overall wellness, yet it’s often overlooked until complications set in. Many cardiovascular diseases, particularly those linked to cholesterol imbalance, develop quietly over time. Understanding conditions like hypercholesterolemia and taking timely steps toward healthier living can go a long way in protecting your heart and ensuring a stronger cardiovascular future.”
Understanding Hypercholesterolemia
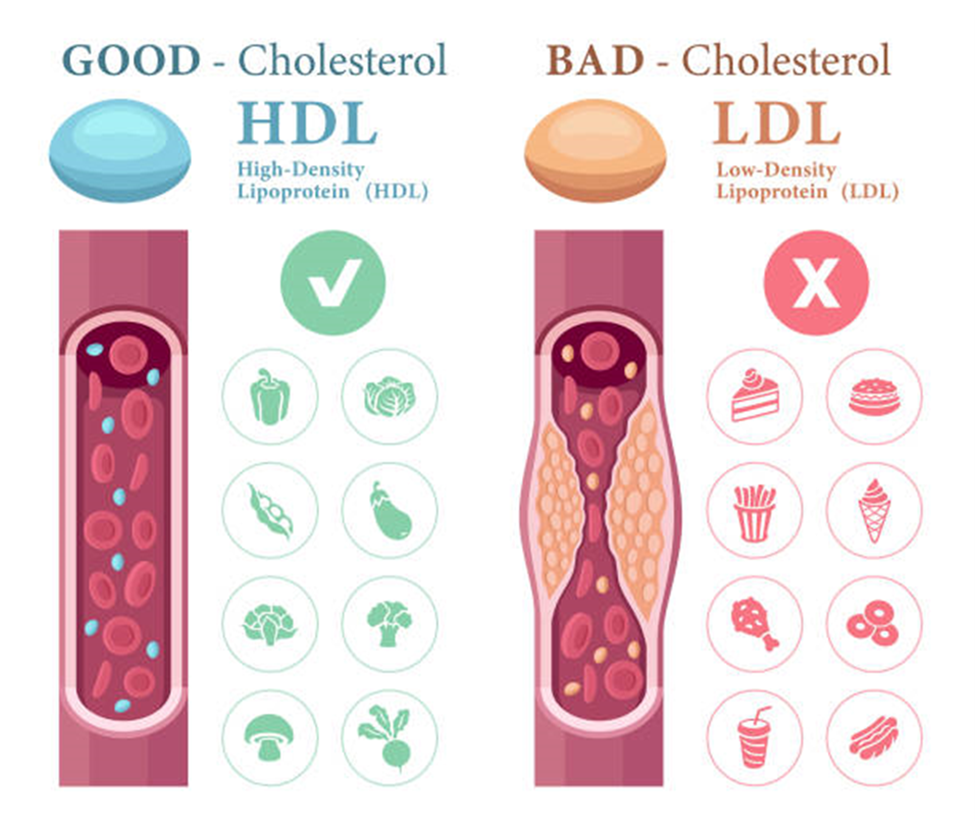
“Understanding cholesterol types is key. HDL helps clear cholesterol from arteries, while LDL deposits it. When cholesterol levels rise abnormally, it can quietly strain the arteries and affect circulation. So, treatment focuses on improving this ratio, not just lowering overall cholesterol.”
What are the Symptoms of Hypercholesterolemia?

Here are a few possible signs:
- Yellowish deposits on the skin or around the eyes (xanthomas).
- Chest pain or angina, especially during exertion.
- Numbness in extremities, due to reduced blood flow.
- Early fatigue and breathlessness, signaling heart strain.
Dr. Chandra notes, “Many people assume they’re fine because they feel fine, but cholesterol damage is slow and silent. Routine screenings, especially for individuals with diabetes or a family history of heart disease, are critical to early detection.”
What are the Causes of Hypercholesterolemia?
Hypercholesterolemia can arise from both genetic predispositions and lifestyle factors. Let’s explore the main contributors:
Unhealthy Diet: High intake of saturated fats, red meat, and processed foods can raise LDL levels.
Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles lower HDL levels and increase triglycerides.
Smoking and Alcohol: These habits damage arterial walls and worsen cholesterol levels.
Obesity: Extra fat around the abdomen contributes to insulin resistance, raising LDL.
Medical Conditions: Diabetes, hypothyroidism, and liver diseases often lead to abnormal cholesterol levels.
Genetic Factors: Familial hypercholesterolemia, a hereditary condition, can cause extremely high cholesterol from a young age.
Dr. Ayush Chandra, a well-known Diabetic Foot Specialist in Ghaziabad, explains, “While genetics play a role, lifestyle choices often amplify the risk. Even with a family history, healthy habits can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing severe complications.”
Managing Hypercholesterolemia
Managing high cholesterol involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical guidance. Here’s what experts recommend:
Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet: Focus on fiber-rich foods, omega-3 fats (found in fish, walnuts, flaxseeds), and plant-based meals.
Stay Active: Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise five days a week — brisk walking, cycling, or swimming works well.
Quit Smoking: This single step can drastically improve HDL levels and vascular health.
Limit Alcohol: Excessive drinking affects triglycerides and liver function.
Monitor Regularly: Schedule regular lipid profile checks to track progress.
Dr. Chandra says, “Sustainable management isn’t about short-term diets but long-term commitment. Even small, consistent changes — like choosing fruits over fried snacks — can create lasting benefits.”
Can Hypercholesterolemia be Treated Permanently?
The idea of a “cure” can be misleading. Hypercholesterolemia is a chronic condition, meaning it can be controlled but not always permanently reversed — especially if it’s genetic. However, for lifestyle-related cases, cholesterol can often return to normal ranges with sustained efforts.
Medical studies suggest that up to 70% of cholesterol improvement depends on lifestyle, while the remaining 30% may require medication.
Dr. Ayush Chandra, a reputed Diabetologist in Ghaziabad, emphasizes, “While we may not always ‘cure’ high cholesterol, we can certainly control it to the point where it no longer threatens your heart. Think of it as a lifelong partnership between you and your healthcare team.”
Treatments Options for Hypercholesterolemia
When diet and exercise alone don’t suffice, doctors may recommend medications or advanced therapies. Common treatment options include:
Statins: These lower LDL levels by reducing cholesterol production in the liver.
Bile Acid Sequestrants: Help remove cholesterol from the body through digestion.
Ezetimibe: Reduces cholesterol absorption from food.
PCSK9 Inhibitors: Modern injectable drugs used in severe or genetic cases.
Niacin & Fibrates: Useful for improving HDL and lowering triglycerides.
Dr. Chandra notes, “Medications are not lifelong punishments but tools. Many patients can reduce or even stop them under supervision once their lifestyle improves and cholesterol stabilizes.”
When to Contact a Doctor
You should consult a doctor if you:
- Have a family history of early heart disease or stroke.
- Are diabetic or hypertensive.
- Notice yellow deposits around eyes or skin.
- Experience chest pain or persistent fatigue.
Regular check-ups are key to prevention. Early diagnosis can prevent heart attacks, strokes, and artery blockages.
Conclusion
Hypercholesterolemia is not a life sentence — it’s a manageable condition. With informed choices, regular follow-ups, and professional guidance, you can lead a healthy life free from cholesterol-related complications.
FAQs
- Can hypercholesterolemia be reversed?
In many lifestyle-related cases, yes. With consistent diet and exercise, LDL levels can drop significantly. However, genetic cases require ongoing management.
- Can exercise lower cholesterol levels?
Absolutely! Regular aerobic activity boosts HDL and helps clear LDL from the bloodstream.
- Is high cholesterol hereditary?
Yes, familial hypercholesterolemia is inherited and can present at an early age. Genetic testing and family screening are recommended.
- What are the risks of untreated hypercholesterolemia?
Untreated cases can lead to artery blockage, heart attack, or stroke due to plaque buildup.
- Can stress affect cholesterol levels?
Yes. Chronic stress can raise LDL and triglycerides, indirectly contributing to high cholesterol. Relaxation techniques like yoga and meditation can help balance it.
References:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23921-hypercholesterolemia
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/symptoms-causes/syc-20350800
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.